The middle layer of the heart wall is called myocardium. Describe the structure of heart rashmiray1981 rashmiray1981 3 minutes ago Biology Secondary School answered a 4.
Structure And Function Of The Heart
Its about the size of ones fist.

. More external--attached to the diaphragm and blood vessels-Composed of dense connective tissue. Structure and function of the heart Structure and function of the heart Structure and function of the heart Rev Esp Cardiol. Superior blood receiving chambers receives blood from veins each has an auricle a ear-shaped structure that increases the capacity of the atrium.
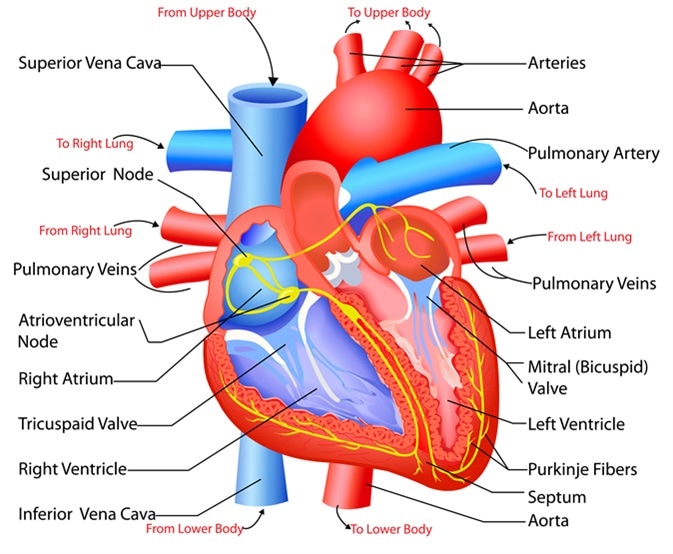
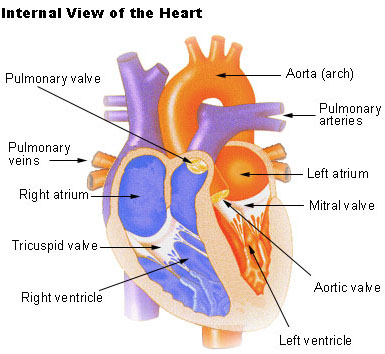
The heart wall is made up of three layers. The two upper thin-walled chambers Auricle or Atria and the lower thick-walled chambers ventricles. Describe the structure of the human heart.
It is located in the centre of the chest cavity slightly bent towards the left. The myocardium consists of the heart muscle cells that make up. The blood is forced out through the SL valves into the artieries.
The two auricles are separated by an interatrial septum and the two ventricles are separated by the interventricular septum. Square6 Superficial layer-Fibrous pericardium. The heart is located in a space in the thoracic cavity between the lungs called the mediastinum.
It has four chambers upper two chambers are called Atria and lower two chambers are called Ventricles. Article in Spanish Author F Torrent-Guasp 1 Affiliation. Each side of the heart consists of an atrium and a ventricle which are two connected chambers.
The human heart is situated to the left of the chest and is enclosed within a fluid-filled cavity described as the pericardial cavity. The atria plural of atrium are where the blood collects when it enters the heart. The pericardium is a fibre membrane found as an external covering around the heart.
The inner layer of the heart wall is called endocardium. Coverings of heart - Pericardium square6 Double walled fibro-serous sac that encloses the heart and great vessels. Epicardium- This is a protective layer made of connective tissues.
The human heart consists of a pair of atria which receive blood and pump it into a pair of ventricles which pump blood into the vessels. The atria and ventricles fill with blood from vena cava and pulmonary vein. The heart is composed of three layers.
Heart Anatomy Heart Wall. Describe the location of the heart and name the space it resides in. From the upper body.
The heart is primarily made of a thick muscle layer called the myocardium surrounded by membranes. How is the variation adaptive. The heart has two atria that fill in as accepting chambers and two ventricles that fill in as siphoning chambers.
The depression among it and the heart is loaded up with pericardial liquid which lessens grinding between the sac and thumping heart. The size of the heart is about the clenched fist. Myocardium- This layer forms the heart muscles.
The muscular middle layer of the wall of. One-way valves separate the four chambers. The two atria are separated from each other by a thin muscular wall called the inter-atrial septum and the right and left ventricles are by a thick-walled inter-ventricular septum.
These are the structures and functions of the Heart. Now up your study game with Learn mode. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from different parts of.
Name the membranous sac that encloses the heart. It is a four-chambered muscular organ protected by a double walled membranous sac pericardium. The outer layer of the heart wall is called epicardium.
The heart has four chambers two relatively small upper chambers called atria and two larger lower chambers called ventricles. - The heart contains four distinct chambers. The walls and lining of the pericardial cavity are made up of a membrane known as the pericardium.
Explain the movement of blood flow through the heart lungs and body. You just studied 38 terms. Cardiac conduction is the rate at which the heart conducts electrical impulses.
It comprises four chambers. The human heart is divided into four chambers. The human heart is four-chambered.
Inelastic Protects the heart from sudden overfilling Pierced superiorly by the aorta SVC. The Heart Structures and Functions. The epicardium the myocardium and the endocardium illustrated in Figure 1.
Heart is the pumping organ in the blood circulatory system. The chambers are separated by a septum. Heart is the organ in the human body that acts as a double pump.
The lower two chambers of the heart are called ventricles. STRUCTURE OF HUMAN HEART. A large vein carrying deoxygenated blood into the heart.
It is situated in the thoracic cavity in between the lungs slightly tilted to the left. The outer layer of the wall of the heart. And the lower two chambers are called the right and left ventricle.
The higher pressure in the arteries closes the SL valves. Two atria and two ventricles. Your answer should be specific.
Atria upper chambers Ventricles lower chambers Layers of heart. The walls of the heart are composed of an outer epicardium a thick myocardium and an inner lining layer of endocardium. The walls of the ventricles are relatively thicker than atrial walls.
The organs of the circulatory system are the heart arteries veins and capillaries. Describe the structure of heart 2 See answers Advertisement Advertisement rashmiray1981 is waiting for your help. The upper two chambers of the heart are called auricles.
The inner wall of the heart has a lining called the endocardium. The Cardiac cycle is the. Its encased in an intense membranous sac called the pericardium.
How does the direction of blood flow blood pressure total area and flow velocity differ between arteries capillaries and veins. In humans the heart is about the size of a clenched fist and it is divided into four chambers. The human heart is a mesodermally derived hollow muscular organ.
The upper two chambers are called right and left atrium. Leftright atria leftright ventricles-atria. The left atrium receives the oxygenated blood from the lungs via the pulmonary vein.
The wall of the heart is made up of three layers. Add your answer and earn points.

Knowledge Of The Structure And Function Of Heart Definition Examples Diagrams

0 Comments